by Chen Sagiv, PhD; Co Founder & Co CEO, DeePathology Ltd
The 3rd Industrial Revolution, also known as the Digital Revolution refers to the shift from analogue electronic technology to digital electronics which began in the second half of the 20th century.
One of the most important aspects of the digital revolution is the availability of personal computers. In the first compute revolution, around the 60s and the 70s, computers were big room-sized machines costing hundreds of thousands of dollars that were operated by white lab coats dressed specialized technicians. Most people had no direct contact with computers, and the machines were popularly viewed as impersonal giant brains that threatened to eliminate jobs through automation. The idea that anyone would have his or her own desktop computer was generally regarded as science fiction.
Then in the 70s, the personal computer (PC) was introduced with size, capabilities, and price that made it feasible for individual use. This was the 2nd computer revolution. The PC was intended to be operated directly by the end user, rather than by a computer expert or technician. Moreover, while users could develop their own applications they did not have to write their own programs but could use commercial or free software which is provided in "ready-to-run" form.
Personal computers and nowadays mobile and fixed workstations provide tremendous compute resources. We have come a long way to allow anyone to have access to personal compute platforms.
We can observe similar trends in the 4th Industrial Revolution - the AI revolution. The mathematical infrastructure for AI and deep learning technology was already established in the 80s last century. However, it took a long time until AI technology made a breakthrough in 2012, as a result of outstanding compute power and availability of large amounts of data. Indeed, AI and big data analysis really changed the world: from speech recognition systems to medical applications. We view it as the 1st AI revolution where it is the huge companies that have access to significant compute power and large amounts of data in order to develop AI solutions. It is common to think that in order to develop AI based solutions you need skilled R&D teams, large data sets, access to strong hardware and that it will take long development cycles to have complete solutions.
How all of this is related to pathology? Let’s start with the Digital Revolution. For more than 150 years pathologists were active in the analogue domain: the glass slides generated from biopsies were studied under a microscope. The Digital Scanners that transform the physical slide into a digital one are the enablers that brought the Digital Revolution to Pathology. This is great ! Pathologists can now view pathology slides on a computer screen, from any location outside the lab and also send pathology images via email for consultation. However, digitization holds the promise for the introduction of image analysis and AI algorithms to pathology, and these two concepts: Digitization & Algorithms are game changers in pathology.
The 1st AI revolution in Pathology was within the territory of companies that need to invest a lot of money in skilled R&D teams and access to significant amounts of data to create their algorithms. These companies usually consult with pathologists to address the right problems,and get the needed data and accompanying annotations. And that sums up the role of the pathologist. The pathologist is NOT taking a part in the actual creation of the algorithms. The creation of the algorithms is in the playground of the AI experts. But now, we face the 2nd AI revolution where AI solutions for pathology can and will be developed by the….. pathologists!
In order to better understand how this can be done, let’s explore how AI solutions are currently developed for pathology. AI companies devote a lot of R&D time and resources to obtain and annotate huge amounts of data to solve ONE important problem. Eventually, they provide a black box solution, for example for prostate cancer, and when they try to make it work in a new lab, it may fail as the whole slide image may appear different from the data the algorithm was trained on.
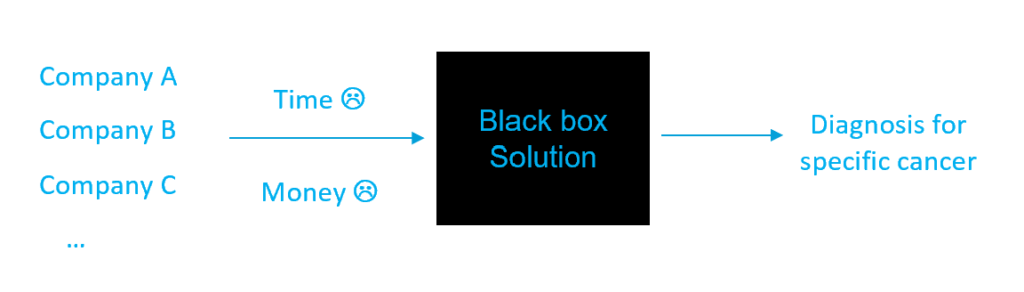
But honestly, pathology has thousands of tasks waiting for possible AI solutions and these solutions should be able to adapt to specific lab conditions. This is where the Do It Yourself platforms enter the game and play a significant. They allow pathologists and researchers to create thousands of AI powered solutions for pathology - by themselves – having the pathologist in the center of the AI solutions creation!
The main vision of the 2nd AI revolution is to bring AI solutions creation capabilities to every pathologist and every pathology lab. Using the Do It Yourself platforms the pathologist will be able to test new ideas, look for different types of cells, structures and tissues, quickly provide quantitative answers to research questions and get immediate feedback while using the limited data they have in the lab and using relatively modest compute resources. The essence of the 2nd AI revolution is to democratize AI and allow pathology experts who are not necessarily AI experts to have access to state-of-the-art AI technology.
Disclaimer: In seeking to foster discourse on a wide array of ideas, the Digital Pathology Association believes that it is important to share a range of prominent industry viewpoints. This article does not necessarily express the viewpoints of the DPA, however we view this as a valuable point with which to facilitate discussion.
2 comment(s) on "The 2nd AI Revolution is on & is making its way to Pathology Putting the pathologist in the center!"
08/25/2020 at 08:00 PM
Bassel says:
Nice article. Very interesting perspective to see the evolution of digital pathology and AI. One question is what are some examples of the mentioned Do it yourself platforms? Any recommendation?09/23/2020 at 08:00 PM
Chen Sagiv says:
In reply to Bassel.Dear Bassel,
As a co founder of DeePathology that is providing such a Do It Yourself platform, the STUDIO, I will refrain from giving any recommendations, but let me mention the players in the eco system
1. DeePathology
2. Aiforia
3. Indica Labs
4. Airamatrix
Please log in to your DPA profile to submit comments